Summer Health Risks and How to Avoid Them
Introduction:
During summer, people often look forward to enjoying themselves during sunny days outdoors. But there are specific health risks that come with this season as well. These include high temperatures, outdoor activities, and a change of routine all which could lead to various health complications. Summer becomes safe and enjoyable when these hazards are well understood and properly managed. This article looks at common summer health problems and gives useful advice to avoid them.
Dehydration and Heat-Related Illnesses
Heat exhaustion and heatstroke are the two conditions that can occur due to dehydration which is the most significant risk in summer.
Dehydration
Causes: High temperatures, physical activity increase, low fluid intake
Symptoms:
Thirsty mouth, parched lips, passing dark urine, feeling dizzy and tired.
Prevention:
Drink plenty of water: At least eight glasses a day unless you’re exercising or in hot weather.
Eat hydrating foods: Watermelon,papayas, tomatoes, cucumbers, vineyards, strawberries, carrots, lettuce, pineapples, oranges, grapes.
Avoid Dehydrating Beverages: Stop alcohol intake, caffeine intake and sugary drinks.
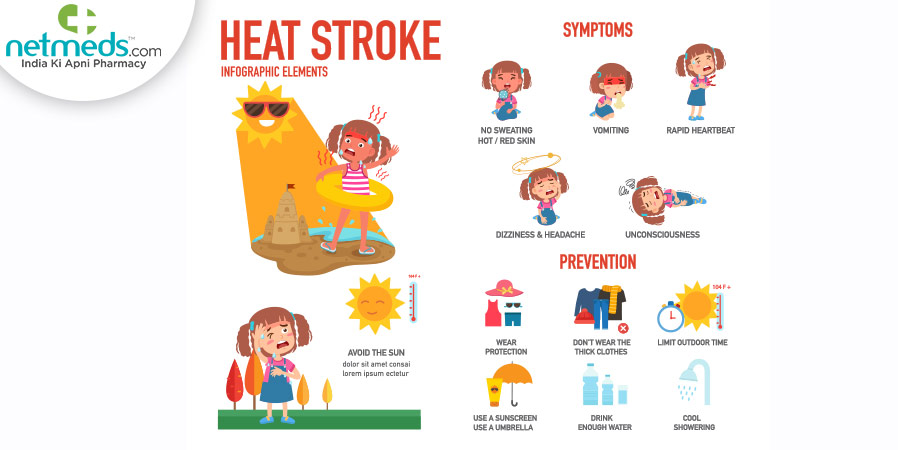
Heat Exhaustion and Heatstroke
Causes: Prolonged exposure to high temperatures, especially during physical activity.
Symptoms:
– Heat Exhaustion: Heavy sweating, weakness, cold and clammy skin, fast and weak pulse, nausea or vomiting, and fainting.
– Heatstroke: High body temperature (above 103°F), hot and dry skin, rapid and strong pulse, confusion, and unconsciousness.
Prevention:
– Stay Hydrated: Drink water regularly, even if you don’t feel thirsty.
– Wear Appropriate Clothing: Choose lightweight, loose-fitting, and light-colored clothing.
– Take Breaks: Rest in shaded or air-conditioned areas to cool down.
– Limit Strenuous Activity: Avoid heavy exercise during peak heat hours (10 a.m. to 4 p.m.).
Sunburn and Skin Damage
Prolonged exposure to the sun’s ultraviolet (UV) rays can cause sunburn and increase the risk of skin cancer.
Sunburn
Causes: Exposure to UV radiation from the sun.
Symptoms: Red, painful skin that feels hot to the touch, swelling, blistering, and peeling.
Prevention:
– Use Sunscreen:Apply broad-spectrum sunscreen with at least SPF 30, and reapply every two hours or after swimming or sweating.
– Wear Protective Clothing: Wear hats, sunglasses, and long-sleeved shirts when possible.
– Seek Shade: Stay in the shade during peak sun hours.
– Avoid Tanning Beds: Use self-tanning products instead of tanning beds, which also emit harmful UV radiation.
Insect Bites and Stings
Summer is the peak season for insects, and bites and stings can lead to allergic reactions and diseases.
Common Insects
Mosquitoes: Can transmit diseases like West Nile virus, Zika virus, and Lyme disease.
Ticks:Can carry Lyme disease and other tick-borne illnesses.
Bees and Wasps: Can cause painful stings and allergic reactions.
Prevention:
– Use Insect Repellent: Apply repellent containing DEET, picaridin, or oil of lemon eucalyptus.
– Wear Protective Clothing:Long sleeves and pants can help prevent bites and stings.
– Avoid Scented Products: Insects are attracted to scented lotions and perfumes.
– Check for Ticks: After spending time outdoors, check your body and clothing for ticks and remove them promptly.
Foodborne Illnesses
Warm temperatures can cause food to spoil faster, increasing the risk of foodborne illnesses.
Common Causes: Bacteria such as Salmonella, E. coli, and Listeria.
Symptoms: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and fever.
Prevention:
– Proper Food Handling: Wash hands, utensils, and surfaces often.
– Safe Food Storage: Keep perishable foods refrigerated and avoid leaving them out for more than two hours (one hour if the temperature is above 90°F).
– Cook Food Thoroughly: Use a food thermometer to ensure meats are cooked to the appropriate internal temperature.
– Avoid Cross-Contamination: Keep raw meats separate from other foods.
Allergies
Pollen, mold, and insect bites can trigger allergies during the summer.
Common Allergens: Grass pollen, ragweed, mold spores, and insect venom.
Symptoms:Sneezing, runny or stuffy nose, itchy eyes, and skin rashes.
Prevention:
– Limit Exposure: Stay indoors during peak pollen times (early morning and windy days).
– Keep Indoor Air Clean: Use air conditioning and keep windows closed.
– Shower After Outdoor Activities: Wash off pollen and other allergens.
– Use Allergy Medications: Antihistamines and nasal sprays can help manage symptoms.
Swimming and Water Safety
Swimming is a popular summer activity but comes with risks such as drowning and waterborne illnesses.
Drowning
Causes: Lack of swimming ability, lack of barriers (like pool fences), lack of supervision, and alcohol use.
Prevention:
– Learn to Swim: Ensure everyone in your family knows how to swim.
– Supervise Children: Always watch children when they are in or near water.
– Use Life Jackets: Wear life jackets when boating or in open water.
– Avoid Alcohol: Don’t drink alcohol before or during swimming.
Waterborne Illnesses
Causes: Bacteria, viruses, and parasites in contaminated water.
Symptoms: Diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and stomach cramps.
Prevention:
– Avoid Swallowing Water: Don’t swallow water from pools, lakes, or the ocean.
– Shower Before Swimming: Rinse off before entering pools to remove dirt and germs.
– Keep Pools Clean: Follow proper pool maintenance and hygiene practices.
Exercise and Physical Activity
Staying active is important, but exercising in hot weather can be risky.
Risks: Heat exhaustion, heatstroke, dehydration, and sunburn.
Prevention:
– Exercise During Cooler Times: Early morning or late evening is best.
– Stay Hydrated: Drink water before, during, and after exercise.
– Wear Appropriate Clothing: Light, breathable, and moisture-wicking fabrics.
– Listen to Your Body: Stop exercising if you feel dizzy, nauseous, or overly fatigued.
Travel Health
Summer is a popular time for travel, which can expose you to different health risks.
Common Risks: Motion sickness, traveler’s diarrhea, and infections.
Prevention:
– Research Destinations: Know the health risks and necessary vaccinations for your travel destination.
– Pack a Health Kit: Include medications, first aid supplies, insect repellent, and sunscreen.
– Stay Hydrated: Drink bottled or purified water to avoid waterborne illnesses.
– Eat Safely: Choose cooked foods and avoid street food in areas with poor sanitation.
Practical Tips for a Healthy Summer
- Stay Informed: Be aware of weather forecasts and health advisories.
- Be Prepared: Have a plan for emergencies, including knowing the location of the nearest medical facilities.
- Educate Yourself: Learn the signs and symptoms of common summer health risks.
- Practice Good Hygiene: Wash your hands frequently, especially before eating and after using the restroom.
- Use Protective Gear: Sunscreen, insect repellent, hats, and sunglasses are essential for outdoor activities.
Conclusion
While summer is a great time to enjoy the outdoors and take part in a variety of activities, there are certain health risks to be aware of and take precautions against. You can reduce these risks and have a safe and enjoyable summer by managing your allergies, staying hydrated, protecting your skin, avoiding insect bites, handling food safely, exercising sensibly, making sure you’re safe around water, and packing appropriately. To maximize the benefits of the sunny season, always remember to be proactive and knowledgeable about your health.